Kin_Scara2_Z (FB)¶
- FUNCTION_BLOCK Kin_Scara2_Z IMPLEMENTS ISMPositionKinematicsInternal,
ISMPositionKinematics_Offset2, ISMKinematicWithConfigurations4, ISMKinPeriodHandling, ISMKinematicWithInfo2
Transformation FB for Scara2 kinematics with an additional axis.
The Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arm (SCARA) is a special type of industrial robot which resembles a human arm. A Scara2 system exhibits two axes and two degrees of freedom. The motion is limited to the X-Y-plane.
Machine coordinate system (MCS) |
|
|---|---|
Origin |
The intersection of axis 0 and the X-Y-plane. |
X |
Defined by the direction the first arm points to when the first rotary axis (a0) is at 0°. |
Y |
The Y axis results automatically from the definitions of the X and Z axis by rotating the X axis by +90° around the Z axis. |
( Z ) |
This FB features an additional linear axis (a2) perpendicular to the X-Y-plane. The Z axis corresponds directly to the positive direction of this additional axis. |
The location of the tool coordinate system (TCS) relative to the MCS in zero position:
Tool coordinate system (TCS) |
|
|---|---|
Origin |
Relative to MCS: dX = dArmLength1 + dArmLength2 dY = 0 dZ = 0 |
X |
Along the X-Axis of the MCS in positive direction |
Y |
Along the Y-Axis of the MCS in positive direction |
Z |
Along the Z-Axis of the MCS in positive direction |
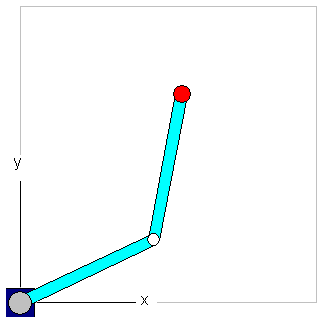
The system consists of
a rotary axis a0 that turns the robot around the Z axis,
the first joint with length dArmLength1,
a second rotary axis a1 that turns the following parts of the robot around the Z axis,
the second joint with length dArmLength2 and
a linear axis (a2) that is orientated in direction of Z.
There are two configurations that can be switched with the input xElbowRight of Kin_Scara2_Z_Config.
The single axes values have the following interpretation:
a0 |
position of the first rotary axis around Z in degrees (A1) |
a1 |
position of the second rotary axis around Z in degrees (A2) |
a2 |
position of the linear axis in direction of Z axis (Z) |
The zero position of the kinematics can be adjusted by defining
constant offsets for the axes. See inputs dOffsetA1, dOffsetA2
and dOffsetZ.
Changing the offsets affects the location and orientation of the TCS.
Note
If this kinematics is used without an orientation-kinematics, then it is not compatible with tools (see SMC_GroupSetTool) that have a position offset in a direction other than the Z direction.
- Attributes:
sm_kin_libdoc- InOut:
Scope
Name
Type
Comment
Input
dArmLength1LREALArm length of 1st joint
dArmLength2LREALArm length of 2nd joint
dOffsetA1LREALAdditional offset of axis A1. This offset is subtracted before the forward transformation and added after the inverse transformation.
dOffsetA2LREALAdditional offset of axis A2. This offset is subtracted before the forward transformation and added after the inverse transformation.
dOffsetZLREALAdditional offset of axis Z. This offset is subtracted before the forward transformation and added after the inverse transformation.
Properties:
Methods:
Structure:
- ActivateAutomaticRotaryPeriods (Method)
- AxesToCartesian (Method)
- AxesToConfiguration_Offset (Method)
- AxesToOrientation (Method)
- CPConnectible (Method)
- CartesianToAxes (Method)
- CartesianToAxes_Offset (Method)
- GetAxisProperties (Method)
- GetConfigurationDataSize (Method)
- GetDefaultConfigurationData (Method)
- GetKinematicsName (Method)
- GetOrientationImage (Method)
- GetPeriods (Method)
- IsConfigSingular (Method)
- IsSingularity (Method)
- NumAxes (Property)
- ProjectPosition (Method)