Element: Generalization
A Generalization is a UML relationship that expresses inheritance or specialization. The inheriting element has the attributes and operations of the root element. In IEC code, this relationship corresponds to the keyword EXTENDS.
A generalization points from the inheriting class to the root class. Therefore, the direction of the arrow indicates who inherits from whom.
A function block can inherit from another function block.
An interface can inherit from another interface.
A DUT can inherit from another DUT.
Programs and functions cannot inherit and be inherited.
Display as arrow
Properties
Relationship | Relationship type |
Optimise route | When this option is selected, the route of the relationship arrow is optimized automatically. The fixed points are the initial point at the start element and the final point at the end element. For example, if the end element is moved, then the point where the arrow points to the end element remains the same. When this option is deselected, the route remains unchanged. As soon as a relationship element is positioned manually in the class diagram, this option is deselected. Select this option if automatic optimization is required. |
Start element | Name of the element where the relationship element starts |
End element | Name of the element that the relationship element points to |
Identifier | For the Association and Composition relationships only Name of the relationship element |
User input
Action | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| A generalization is drawn between the heir and the parent element. The IEC code is adapted synchronously by specifying the parent element in the declaration part of the inheriting class. Example: | |
| A generalization is drawn between the heir and the parent element. The IEC code is adapted automatically by creating the new object and specifying the parent object in the declaration part of the inheriting object. Example: NoteThis input does not work for the DUT element. | |
| The lines are changed. The Optimise routing property is deselected automatically. | |
| The generalization is removed from the diagram and IEC code. The statement | |
Example
Fb_A inherits from Fb_Base:
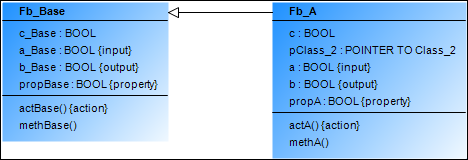
FUNCTION_BLOCK Fb_A EXTENDS Fb_Base
Itf_A inherits from Ift_Base:
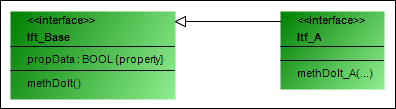
INTERFACE Itf_A EXTENDS Itf_Base
Dut_A inherits from Dut_Base:
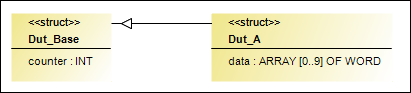
TYPE Dut_Base :
STRUCT
counter : INT;
END_STRUCT
END_TYPE
TYPE Dut_A EXTENDS Dut_Base :
STRUCT
data : ARRAY[0..9] OF WORD;
END_STRUCT
END_TYPE
