Tutorial: Visualizing a Refrigerator Controller
This tutorial demonstrates how to add visualizations to the project and link the elements of the visualization to the variables of the control program.
Preparation
This tutorial is based on the sample program RefigeratorControl, which was created in the "Your First Program in CODESYS" chapter. The finished program can also be found in the installation directory of CODESYS in the Projects subfolder.
For more information, see the following: Your First CODESYS Program
Creating the visualizations
Visualization: Control elements and display of the refrigeratorDiagnosis: History of the set and actual temperature, parameter settingsLive Visu: Animation with refrigerator
In the device tree, click the
Applicationobject.Click the Project → Add Object → Visualization command.
Specify the name as
Live_Visu.Create two more visualizations with the names
DiagnosisandVisualization.
Structure of the visualization Visualization
This screen consists of control and display elements for the refrigerator.
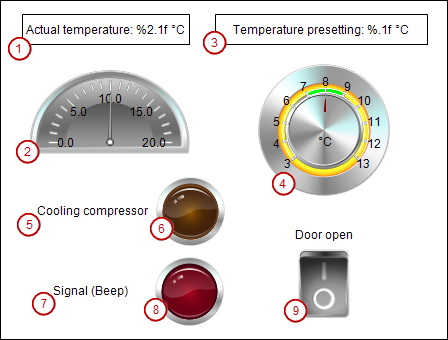
 : Numeric display of the actual temperature
: Numeric display of the actual temperature : Pointer to display of the actual temperature
: Pointer to display of the actual temperature : Numeric display of the set temperature
: Numeric display of the set temperature : Potentiometer for setting the set temperature
: Potentiometer for setting the set temperature : Label for compressor lamp
: Label for compressor lamp : Lamp for compressor on
: Lamp for compressor on : Label for signal lamp
: Label for signal lamp : Lamp for signal "Close doors"
: Lamp for signal "Close doors" : Switch for opening and closing the refrigerator door
: Switch for opening and closing the refrigerator door
Open the visualization
Visualizationin the editor.Drag a Rectangle visualization element into the editor.
. Change the following propertiesTexts → Text:
Actual temperature: %2.1f °CText variables → Text variable:
Glob_Var.rTempActual
Drag a Meter 180° visualization element to the editor.
. Change the following properties:
Glob_Var.rTempActualScale → Scale end:
20Scale → Main scale:
5Scale → Subscale:
1
Drag a Rectangle visualization element to the editor.
. Change the following propertiesTexts → Text:
Temperature presetting: %.1f °CText variables → Text variable:
Glob_Var.rTempSet
Drag a Potentiometer visualization element into the editor.
. Change the following properties:
Glob_Var.rTempSetBackground → Background color: yellow
Pointer → Color: red
Scale → Subscale position: Outward
Scale → Scale start:
3Scale → Scale end:
13Scale → Subscale:
1Scale → Main scale:
1Label → Unit:
°CLabel → Scale format (C syntax):
%.0fLabel → Max. text width of labels:
21Label → Height of labels:
15
Drag a Label visualization element into the editor.
. Change the following propertiesTexts → Text:
Cooling compressor
Drag a Lamp visualization element into the editor. Position it behind the "
Cooling compressor“ text.. Change the following properties:
Glob_Var.bCompressor
Drag a Label visualization element to the editor.
. Change the following propertiesTexts → Text:
Signal (beep)
Drag a Lamp visualization element to the editor. Position it behind the text "Signal (beep)".
. Change the following properties:
Glob_Var.bSignalBackground → Image:
red
Drag a Rectangle visualization element to the editor.
. Change the following properties:
Door open
Drag a Rocker Switch visualization element to the editor.
. Change the following properties:
Glob_Var.rDoorOpen
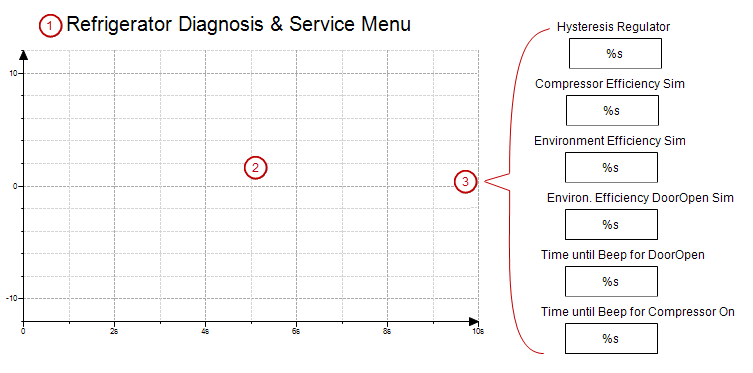
Structure of the visualization Diagnosis
In this screen, you can monitor the temperature curve and optimize the parameters.
Open the visualization
Diagnosisin the editor.Drag a Label visualization element to the editor.
. Change the following properties:
Refrigerator Diagnosis & Service Menu:
Arial, Standard, 18
Drag a Trace visualization element to the editor.
Click the
Diagnosis_Trace1value of the Trace property.The Trace Configuration dialog opens.
Select the
MainTaskin Task.Click the Add Variable link.
A variable is added to the trace. The variable settings are displayed in the dialog.
Select
Glob_Var.bCompressorfor the variable.Add the
Glob_Var.rTempSetandGlob_Var.rTempActualvariables to the trace. For the other settings, you can use the default values.Click OK to exit the dialog.
Drag a Rectangle visualization element to the editor. Position it on he right next to the trace element.
. Change the following propertiesTexts → Text:
%sText variables → Text variable:
PLC_PRG.rHysteresis
Configure the
OnMouseDowninput configuration of the element. Click Input configuration →OnMouseDown→ Configure.The Input Configuration dialog opens.
Assign the Write Variable command to the action. Accept the default values and click OK.
Drag a Label visualization element to the editor. Position it over the first rectangle.
. Change the following propertiesTexts → Text:
Hysteresis Regulator
Adjust the size and position of both elements.
Select both of the Rectangle and Label elements and duplicate them by means of copy and paste.
- . Adjust the labels and variables of the copied elements.
Text:
Compressor EfficiencyText variable:
Simulation.P_CoolingText:
Environment EfficiencyText variable:
Simulation.P_EnvironmentText:
Environ. Efficiency DoorOpen SimText variable:
Simulation.P_EnvironmentDoorOpenText:
Time until Beep for DoorOpenText variable:
Glob_Var.timDoorOpenThresholdText:
Time until Beep for Compressor OnText variable:
Glob_Var.timAlarmThreshold
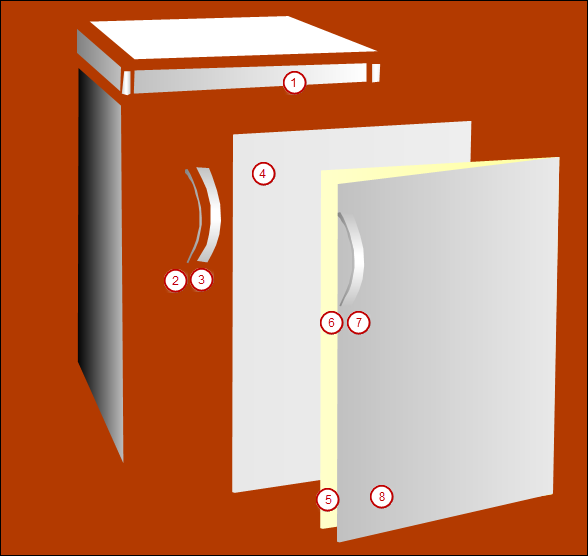
Structure of the Live-Visu visualization
This screen includes the representation of a refrigerator. The refrigerator consists of several polygon type visualization elements. The doors of the refrigerator are drawn in both the closed and open states. Both doors consist of a group of single elements.
Open the visualization
Live_Visuin the editor.Select the Polygon visualization element in the Visualization Toolbox view.
Click several times in the editor to create a surface. Right-click to stop adding corner marks.
Move the corner marks to the required position so that the
 element (1) is formed.
element (1) is formed.
Select the element.
. Change the following properties:Colors → Use gradient color:

Appearance → Line style: Invisible
Click the Colors → Use gradient color property.
In the Gradient Editor dialog, select the color Gray for Color 1.

Create all other elements with the Polygon visualization element.
Group the elements of the closed door (
 ,
,  , and
, and  ) and the elements of the open door (
) and the elements of the open door ( ,
,  ,
,  , and
, and  ). To do this, press the Shift key and click the Visualization → Group command to select the elements.
). To do this, press the Shift key and click the Visualization → Group command to select the elements.Move the elements together so that the completed refrigerator is formed. Position the open doors precisely on the closed doors.
Select the "
Open doors" group.In the properties, double-click the State variable → Invisible input field.
Press the F2 key to open the Input Assistant.
In the Variables category, select the
rDoorOpenvariable (belowApplication→Glob_Var).Negate the variable with
NOT(–>NOT Glob_Var.rDoorOpen).If the
rDoorOpenvariable is FALSE (door is closed), then the element is invisible. Then the underlying doors are visible.When the
rDoorOpenvariable isFALSE(door is closed), the element is invisible. Then the underlying doors are visible.- . Copy the following elements from the
Visualizationscreen:Potentiometer for setting the temperature
Rectangle for displaying the set temperature
Door openswitchCooling compressorlampSignal (beep)lamp
Insert the elements from the clipboard to the
Live_Visuvisualization screen.Reduce the elements and position them on the refrigerator.

Visualization in online mode (simulation)
When the visualization is complete, test it in simulation mode.
Click the Online → Simulation command.
Click the Online → Login command.
A dialog opens and prompts you to create and download the application.
Click Yes to confirm the dialog.
Click Debug → Start.
Open the visualization
Live_Visuin the editor.The refrigerator is in online mode.
Open the doors with the switch and monitor the temperature and the alarms. Change the parameters in the screen
Diagnosisand watch the reaction in the temperature curve.