Visualization Element: Slider
Symbol:

Category: Common Controls
The element changes the value of a variable, depending on the position of the slider within the slider bar. You define the value range of the slider bar by means of the scale start and scale end.
Element properties
Are all element properties available?
All properties are available only after you select the Advanced option or the All categories filter in Properties.
Element name | Example: TipAssign individual names for elements so that they are found faster in the element list. |
Element Type | Slider |
Position
The position defines the location and size of the element in the visualization window. This is based on the Cartesian coordinate system. The origin is located in the upper left corner of the window. The positive horizontal X-axis runs to the right. The positive vertical Y-axis runs downwards.
X | The X-coordinate (in pixels) of the upper left corner of the element Example: |
Y | The Y-coordinate (in pixels) of the upper left corner of the element Example: |
Width | Specified in pixels Example: |
Height | Specified in pixels Example: |
Tip
You can change the values by dragging the box  symbols to other positions in the editor.
symbols to other positions in the editor.
Variable
Variable | Variable (numeric data type) Example: When executed, the variable assigns a value that corresponds to the position of the slider in the bar. |
Page size | . Page size
Requirement: The Move to click element property is not selected. |
Move to click | Behavior of the slider at visualization runtime when it is clicked:
|
Scale
Show scale |
NoteThis property is available for the slider only. |
Scale start | Least value of the scale and the lower limit of the value range for the element Example: 0 TipIn the value field, click the |
Variable | Variable (integer data type) for the scale start Example: |
Scale end | Greatest value of the scale and the upper limit of the value range for the element Example: 100 TipIn the value field, click the |
Variable | Variable (integer data type) for the scale end Example: |
Main scale | Distance between two tick marks on the main scale. Example: 10 TipIn the value field, click the |
Variable | Variable (integer data type) for the spacing Example: |
Sub scale | Distance between two tick marks on the fine scale You can hide the fine scale by setting the value to 0. Example: 2 TipIn the value field, click the |
Variable | Variable (integer data type) for the spacing Example: |
Scale format (C syntax) | Formatting the scale label Example: NoteThis property is available for the slider only. |
Scale proportion | Size of the scale (in %) of the total size |
Note
A valid declaration in the application code is required for the variables used as an example in the table above.
Bar
The property defines the representation of scaling and direction of travel.
Diagram type | The list box varies depending on the alignment of the diagram. . Horizontal
. Vertical
|
Orientation | . Alignment of the slider; defined by the ratio of width to height.
TipYou can modify the alignment in the visualization editor by using the pointing device to adjust the width and height of the scroll bar. |
Running direction | The list box varies depending on the alignment of the slider. . Horizontal
. Vertical
|
State variables
The variables control the element behavior dynamically.
Invisible | Variable (
Example: |
Deactivate inputs | Variable (
|
Tip
The Invisible property is supported by the "Client Animation" functionality.
Center
The properties contain fixed values for the coordinates of the point of rotation. The rotation point is displayed in the editor as the TipYou can also change the values by dragging the | |
X | X-coordinate of the point of rotation |
Y | Y-coordinate of the point of rotation |
Absolute movement
The properties can be assigned to IEC variables for controlling the position of the element dynamically. The reference point is the upper left corner of the element. At runtime, the entire element is moved.
Movement | ||
X |
Increasing this value at runtime moves the element to the right. | |
Y |
Increasing this value at runtime moves the element downwards. | |
Rotation | Variable (numeric data type) for the angle of rotation (in degrees) Example: The midpoint of the element rotates at the Center point. This rotation point is shown as the At runtime, the alignment of the element remains the same with respect to the coordinate system of the visualization. Increasing the value rotates the element to the right. | 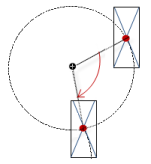 |
Interior rotation | Variable (numeric data type) for the angle of rotation (in degrees) Example: At runtime, the element rotates about the point of rotation specified in Center according to the value of the variable. In addition, the alignment of the element rotates according to the coordinate system of the visualization. Increasing the value in the code rotates clockwise. The rotation point is shown as the NoteIf a static angle of rotation is specified in the property, then the static angle of rotation is added to the variable angle of rotation (offset) when the visualization is executed. | 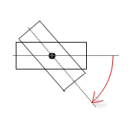 |
Tip
You can combine the variables to a Unit conversion.
Tip
The X, Y, Rotation, and Interior rotation properties are supported by the "Client Animation" functionality.
Animation
Tip
These properties are available only when you have selected the Support client animations and overlay of native elements option in the Visualization Manager.
Animation duration | Variable for the duration (in milliseconds) in which the element runs an animation
. Animatable properties
The animated movement is executed when at least one value of an animatable property has changed. The movement then executed is not jerky, but is smooth within the specified animation duration. The visualization element travels to the specified position while rotating dynamically. The transitions are smooth. |
Move to foreground | Variable (
Example: |
Input Configuration
The properties contain the configurations for the user input when using the mouse or keyboard. A user input defines an event and one or more actions that are executed when an event occurs.
TipThe Configure button opens the Input Configuration dialog. There you can create or edit user inputs. Configured user inputs are listed below the events. They each include the action that is triggered and the setting in short form. Example: Execute ST Code: | |
OnDialogClosed | Input event: The user closes the dialog. |
OnMouseClick | Input event: The user clicks the mouse button completely in the element area. The mouse button is clicked and released. |
OnMouseDown | Input event: The user clicks down on the mouse button. |
OnMouseEnter | Input event: The user drags the mouse pointer to the element. |
OnMouseLeave | Input event: The user drags the mouse pointer away from the element. |
OnMouseMove | Input event: The user moves the mouse pointer over the element area. |
OnMouseUp | . Input events:
NoteThis CODESYS-specific triggering behavior guarantees that actions for key elements are completed. A key element starts an action for OnMouseDown and ends the action for OnMouseUp. Example: A visualization user presses the mouse button within the element area of the key element and then moves the cursor position so that it is located outside of the element area. The action is ended anyway because OnMouseUp is triggered. |
OnValueChanged | Event which triggers follow-up actions due to a change in value Which follow-up actions are triggered is configured in the Input Configuration dialog. The defined follow-up actions and the corresponding configuration are displayed below the element property. The OnValueChanged event can be disabled by the VISU_NO_VALUECHANGED compiler define in the properties dialog of the application. |
Tap | When a mouse click event occurs, the variable defined in Variable is described in the application. The coding depends on the Tap FALSE and Tap on enter if captured options. |
Variable | Requirement: The Tap FALSE option is not activated. Variable (
Example: |
Tap FALSE |
|
Tap on enter if captured |
The value is |
Switch over | With the onset of a mouse click event, the variable is set; when the mouse click event is completed, the variable is reset. |
Variable | Variable ( This is when the user releases the mouse button while the mouse pointer is over the element area. If the user releases the mouse button while the mouse pointer is outside of the element area, then the mouse click event is not ended and the value is not toggled. TipThe user can cancel a started toggle input by dragging the mouse pointer out of the element area. |
Toggle on up if captured |
|
Hotkey | Shortcut on the element for triggering specific input actions When the hotkey event occurs, the input actions in the Events property are triggered. In this way, it is not the input action itself that leads to this input action, but the mouse input action. |
Key | Key pressed for input action. Example: T The following properties appear when a key is selected. |
Events |
|
Switch over |
Example: Shift+T. |
Control |
Example: Ctrl+T. |
Alt |
Example: Alt+T. |
Tip
All keyboard shortcuts and their actions that are configured in the visualization are listed on the Keyboard Configuration tab.
Permissions
Note
Available only when a user management is set up for visualization.
Access Rights button | Opens the Access Rights dialog. There you can edit the access privileges for the element. . Status messages:
|