CNC Example 16: Probing function (clear remaining distance) (G31)
See the CNC16_G31.project sample project in the installation directory of CODESYS under ..\CODESYS SoftMotion\Examples.
The sample project shows how to use the probing function (clear remaining distance).
In the example, the machine moves in the X direction until a light barrier is reached at X=50. As soon as the light barrier has been reached, the machine has to stop. The remaining G-Code has to be processed starting from this position.
Structure of the application
The structure is typical for CNC applications. The G-code is read in the background task (PathTask). Path preprocessing is also done in this task. The interpolation is performed in the bus task (MainTask).
The following G-code is used. In block N10, a rapid positioning is made to X = 20. Then, with G31 (probing function: clear remaining path) , a movement is made to X = 100. Finally, in block N30, a linear movement is made to X = 20, Y = 50.
N10 G0 X20 F100 E1000 E-1000 N20 G31 X100 N30 G1 X20 Y50
The interaction between the interpolator and the interpreter is particularly important for the probing function (clear remaining path).
The interpreter decodes the G-code and generates a straight line from
X=20toX=100for blockN20. Then it stops decoding.The interpolator performs the linear movement and simultaneously outputs the probe number as output
udiActProbe. For the G31, the sample number is always 1.In the application, the interpolator is stopped with
bQuick_Stopas soon as the drive travels beyond positionX=50. (This simulates the light barrier.)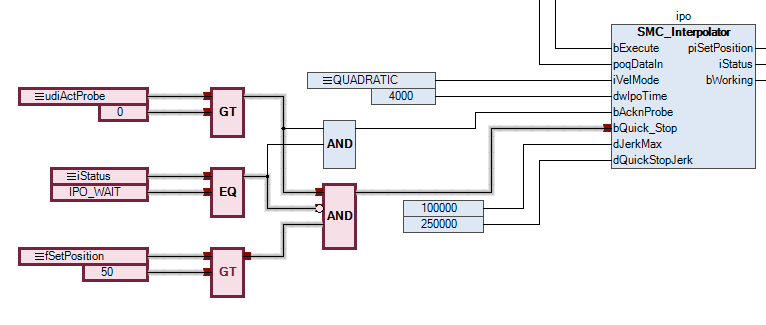
In the bus task, the
SMC_SetInterpreterStartPositionfunction block is used to continuously copy the current position of the machine.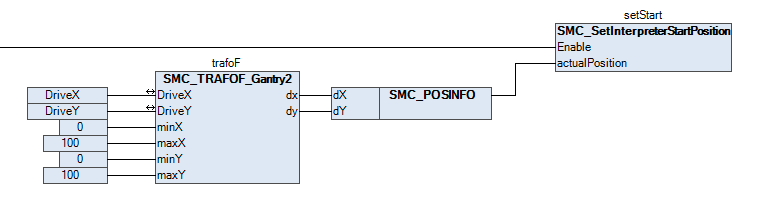
In the
PathTask, the start position is assigned to the inputSMC_NCInterpreter.piStartPosition:inter( sentences:= read.sentences, bExecute:= read.bExecute, nSizeOutQueue:= SIZEOF(bufIpo), pbyBufferOutQueue:= ADR(bufIpo), piStartPosition:= Main.setStart.StartPos);
As soon as the interpolator is stopped, the
bAcknProbeinput is used to acknowledge the G31 command. In a real application, it should also be checked at this point that the axes have actually reached the stop position. The SMC_InPosition function block can be used to do this.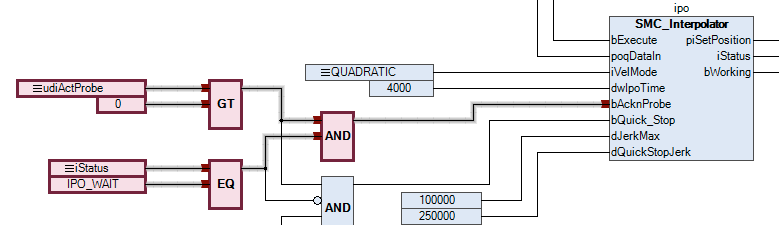
This causes the interpreter to resume decoding, but with the updated start position so that the following block
N30is started from positionX=55.5.
The following diagram illustrates these steps. The numbers in brackets refer to the corresponding steps in the process outlined above.
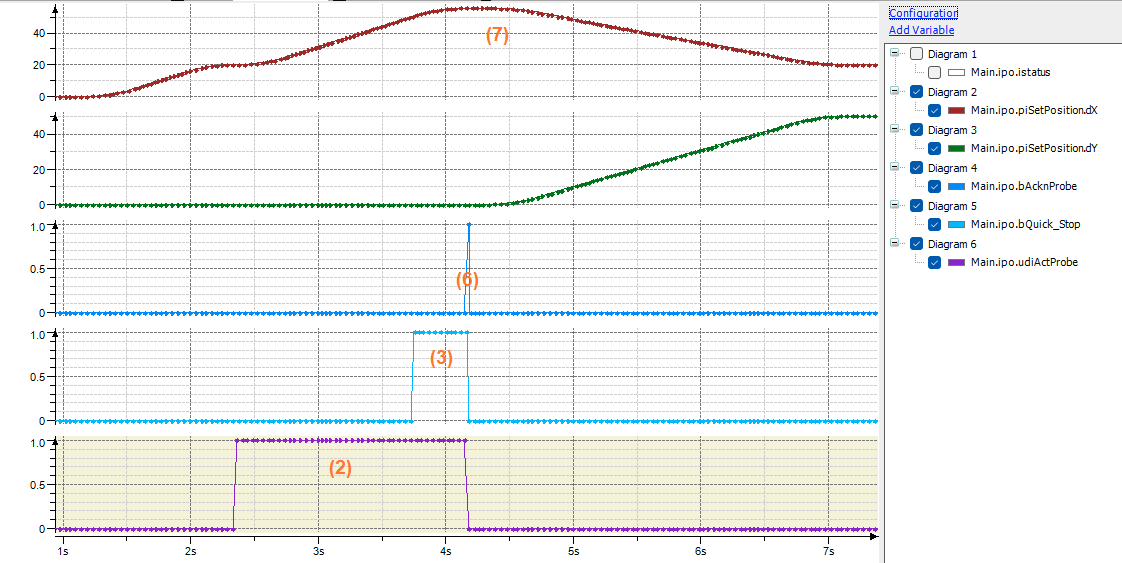
Commissioning
Build the application and download it to a controller.
Open the trace and download it to the controller.
Start the application and open the visualization.