Using Input Assistance
CODESYS provides tools and features to help you code when creating programs.
Input Assistant
The Input Assistant provides all program elements that you can insert at the current cursor position. Open the Input Assistant dialog by clicking or by pressing the F2 key.
Dialog: Auto Declare
This dialog supports the declaration of variables.
For more information, see: Auto Declare
List components
The "List components" function is an input tool in textual editors to help you input valid identifiers. Activate this function by clicking and then the SmartCoding category. Select the List components after typing a dot (.) option.
If you type a dot (
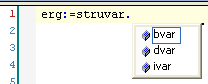
.) instead of a global variable, then a list box opens with all available global variables. You insert the selected variable after the dot by double-clicking a variable in the list box or by pressing Enter.If you type a dot (.) instead of a global variable after a function block instance variable or a structure variable, then CODESYS opens a list box with all global variables, all input and output variables for the function block, or all structure members.
You insert the selected variable after the dot by double-clicking a variable in the list box or by pressing Enter.
Note: When you also want to choose from the local variables of function block instances, select the Show all instance variables in Input Assistant option in the CODESYS options in the SmartCoding category.
If a component access (with a dot) for a list box has already happened, then the last selected entry is preselected at the next component access.
When you type any sequence of characters and then press Ctrl + Space, a list box opens with all available POUs and global variables. The first element in this list that starts with the sequence of characters is selected by default and you can insert it by double-clicking it or by pressing Enter.
Matches with the entered string are highlighted in yellow in the list box.
If the entered string is changed, then the displayed list box is refreshed.
In the ST editor, you can filter the displayed list box by scopes:
Depending on the displayed list box, you can use the Arrow right and Arrow left keys to toggle between the following list boxes:
All items
Keywords
Global declarations
Local declarations
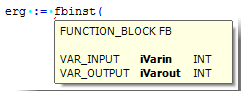
CODESYS displays a tooltip if you type an opening parenthesis for a POU parameter when calling a function block, a method, or a function. This tooltip includes information about the parameters as they are declared in the POU. The tooltip remains open until you click to close it or you change the focus away from the current view. If you accidentally close the tooltip, then you can reopen it by pressing Ctrl + Shift + Space.
Tip
You can use the pragma attribute hide for excluding variables from the "List components" feature.
Typing structure variables:
Calling a function block:
For more information, see: SmartCoding
Short form feature
The short form feature allows you to type short forms for variable declarations in the declaration editor and in textual editors where variables declarations are possible. Use this feature by pressing Ctrl + Enter to end a declaration line.
For more information, see: Shortcuts for Variable Declaration
CODESYS supports the following short forms:
All identifiers become variable identifiers except the last identifier of a line.
The data type of the declaration is determined by the last identifier of the line. The following applies:
b becomes
: BOOLd becomes
: DINTi becomes
: INTl becomes
: LINTr becomes
: REALs becomes
: STRINGs 8 becomes
: STRING(8)with string lengtht becomes
: TIMEu becomes
: UINTw becomes
: WORD
If a data type is not defined using this rule, then the data type is automatically
BOOL, and the last identifier is not used as the data type (see Example 1).Depending on the type of declaration, every defined constant becomes an initialization or string length definition (see Example 2 and 3).
An address, such as
%MD12, is automatically extended with the AT attribute (see Example 4).Any text after a semicolon (
;) is converted into a comment (see Example 3).All other characters in the line are ignored (see exclamation mark in Example 5).
Short Form | Resulting declaration | |
|---|---|---|
1 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
3 |
|
|
4 |
|
|
5 |
|
|
Smart tag functions
Smart tags make it easier to write program code by suggest appropriate commands directly at the programming element. When you place the cursor over a programming element that has a smart tag function, the  symbol appears. When you click the
symbol appears. When you click the  symbol, the commands that you can choose from are shown. Available smart tags:
symbol, the commands that you can choose from are shown. Available smart tags:
The smart tag function provides the Auto Declare command for undeclared variables in the implementation part of the ST editor.