CODESYS J1939 Safety Basics¶
CODESYS J1939 Safety provides functions blocks to build a safe J1939 message transport chain:
Safe_SDG_Producer to produce the J1939-76 Safety Data Group (SDG) message(s).
J1939SafetyStd.Unsafe_SDG_Sender to send the SDG safety / data messages via CAN driver.
J1939SafetyStd.Unsafe_SDG_Receiver to receive selected J1939 safety / data messages and join them to interrelated, unsafe “Safety Data Group” (SDG) data.
Safe_SDG_Consumer to consume unsafe SDG data provided by a J1939SafetyStd.Unsafe_SDG_Receiver, check if they are consistent / safe and provide the transported J1939-76 SDG data to the application.
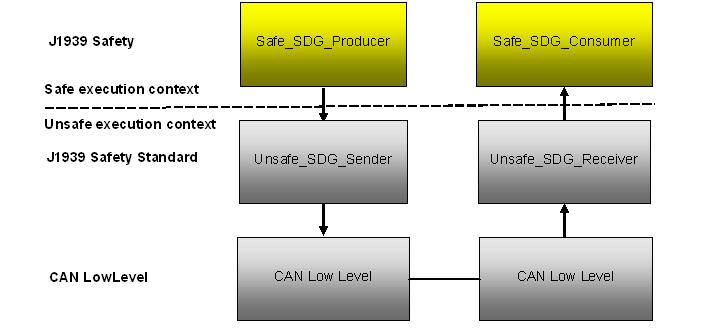
The J1939 safety protocol is implemented in this library according to the SAE J1939 safety specification. However, to use the protocol in a CODESYS safety SIL2 application, it is necessary to consider the entire configuration of the system and to be familiar with the CODESYS Safety SIL2 user manual and the protocol specification.
Recommended Task context¶
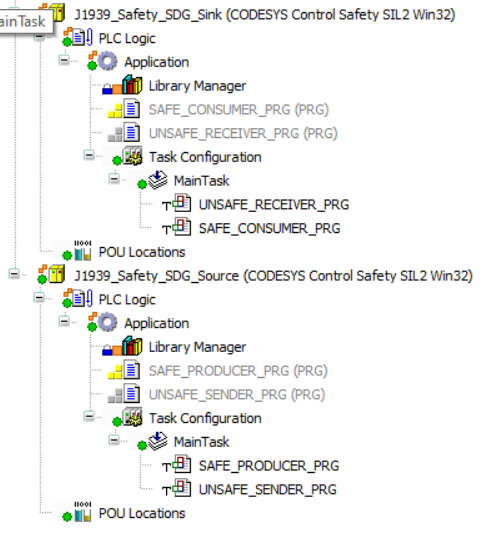
To explain the recommended task context we assume a simple use case. One Safety PLC acts as a “J1939 Safety SDG Source” and a second one acts as “J1939 Safety SDG Sink”. In this case the pair Safe_SDG_Producer / Unsafe_SDG_Sender is supposed to reside on the first Safety PLC (let’s call it “J1939 Safety SDG Source PLC”). The related pair Unsafe_SDG_Receiver / Safe_SDG_Consumer is supposed to reside on second Safety PLC (let’s call ist “J1939 Safety SDG Sink PLC”).
The best performance is achieved when sending SDGs by calling the “Safe PRG” with the Safe_SDG_Producer before the “Unsafe PRG” with the Unsafe_SDG_Sender in one task in this order. Analogous applies for the receive of SDGs the sequence “Unsafe PRG” with Unsafe_SDG_Receiver before the “Safe PRG” with Safe_SDG_Consumer in one Task in this order.
In real world applications a PLC will eventually act as both “J1939 Safety SDG Source” and “J1939 Safety SDG Sink”.
Limitations¶
CODESYS J1939 Safety comes with the following limitations:
SAE J1939-76 limits messages to fixed size (PG data length 8 bytes or less)
SAE J1939-76 applies some constraints regarding PG Transmission Rate (see SAE J1939-76 APR2020 4.4.1 Applicable SAE J1939 Messages), but CODESYS J1939 Safety is limited to “Fixed Transmission Rate PG”
CODESYS J1939 Safety (unsafe part) is utilizing an own CODESYS CAN low level driver instance, a driver instance used somewhere else can not be reused.
Safe_SDG_Producer samples inputs S_dwPGN, S_tTransmissionRate, S_usiSrcAddr, S_usiSHMPriority and S_usiSDMPriority with the rising edge of xEnable, so that these parameters are set for the activated SDG production.
Safe_SDG_Consumer samples inputs S_dwPGN, S_tTransmissionRate, S_usiSrcAddr, S_tSCT and S_tSRVT with the rising edge of xEnable, so that these parameters are set for the activated SDG consumption.
By concept J1939 comes with the limitation that in one network a combination “Parameter Group Number” (PGN) / “Source Address” (of a SDG) needs to be unique. So there must be no SDG with the same combination PGN / “Source Address” within one network.
Examples¶
The CODESYS J1939 Safety library comes with examples to demonstrate usage. To get an idea about the data flow in general please take a look at J1939 Safety example.project -> device ExampleDataFlow -> FUNCTION_BLOCK J1939_example_CFC. To get an idea about how to deal with the separation of safe / unsafe code and relation to a task context please take a look at J1939 Safety example.project -> device J1939_Producer / J1939_Consumer -> Task Configuration -> MainTask.
Therms and Abbreviations¶
Therms and abbrevations see SAE J1939-76 APR2020 3 Definitions and Abbreviations
