Action: ExecuteScript
Function: The action runs a script in the script engine.
Call: Scripting test driver
Tip
When you perform this action in CODESYS V3.5 SP5 or a later version, Python scripts that run through Test Manager support the default script debugging features. For a detailed description, see the help page for the command-line interface. In older CODESYS Test Manager versions, the Test Manager supports only basic debugging by means of automatic detection of. NET-based debuggers such as "Python Tools for Visual Studio PTVS" and "SharpDevelop". If the Test Manager detects that this kind of debugger is connected to CODESYS while the test script is running, then it writes the Python source to a temporary file in the Temp directory and activates the debugging mode of the IronPython engine.
Tab: Python Script
The Python script, which will be executed, is edited in this input area. Input and output parameters can be used as variables in the Python script. 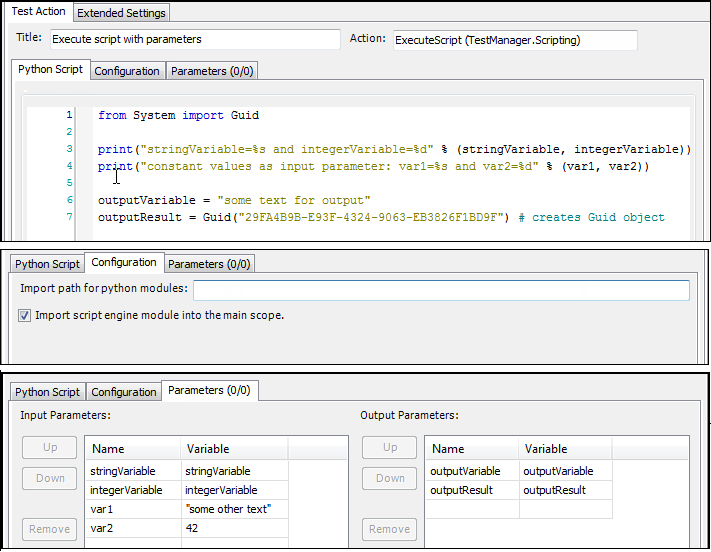 | |
Show tab characters |
|
T<->L | Converts tabs into spacing characters and back |
 | Imports the Python script from an external file |
 | Exports the Python script to an external file The script is saved in the test script by clicking the Save button. |
Check | Syntax check of the Python script If errors or warnings occur, then this is indicated in a corresponding dialog. The cursor is set at the corresponding position in the editor. |
Before the script is executed, the input parameters of this action are copied as defined variables into the scope of the script. After the script is executed, the variables are copied from the scope of the script to the output parameters. If errors occur here, then the action fails.
You can access global variables by means of the object executionContext.GlobalVariables. The following methods are available:
Add(<name>, <object/value>)Contains(<name>)Get(<name>)Set(<name>, <object/value>)Remove(<name>)
executionContext.GlobalVariables.Set("TestVar1", "Some Text")
For more information, see "Python Tools for Visual Studio (PTVS)" and "SharpDevelop" on the Internet.
Tab: Configuration
Import path for Python modules | Paths separated by ";" which are added to the search path for Python modules The Python modules in this path have to be loaded in the script for each import. |
Import script engine modules into main scope | Enabled by default
The option can be disabled to avoid naming conflicts if future updates of CODESYS or if the installation of additional plug-ins introduce additional objects. If this option is disabled, then an explicit import in the Python code can be used for accessing the CODESYS APIs. Beispiel:
from scriptengine import system, projects # import explicitly named members into the main scope
or
import scriptengine # import module
scriptengine.projects.open("d:\test.project") # access the functions qualified by module |
Tab: Parameters
The parameters defined on the Parameters tab are used to exchange values between test script variables and parameters of test actions. Parameters can be used as placeholders on the Configuration tab. For this, the name of the parameter is set in braces in the configuration dialog. Example: {name}.
Tip
Variables defined globally in the script (with the prefix $GLOBALS.) can be used directly in the test action. It is not necessary to use input parameters for passing. Using output parameters is necessary for writing global variables.
Input parameters: When executing the test action, the values of the test script variables are passed to the input parameters of the test action and can be used in the configuration of the test action. | |
Output parameters: When executing the test action, the values of the output parameters of the test action are passed to the test script variables and can be used (for example, in other test actions). | |
Name | Name of the input/output parameter This name is defined in addition to the variable name to identify the origin of the parameter when it is passed to another script. During the test run, this name is displayed as the Outer name on the Variables (scope #<n>) tab in the Test progress window. Background: When a script To see that this variable is recognized as variable |
Variable | Name of the test script variable Example: |
Move Up | Moves the selected variable one line up |
Move Down | Moves the selected variable one line down |
Remove | Removes the selected variable from the list |
