Modifiers and Operators in IL
Modifier | Combined with operator | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
| The command is executed only when the result of the preceding expression is |
|
| The command is executed only when the result of the preceding expression is |
| Otherwise | Negation of the operand (not of the accumulator) |
Operator | N | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
|
| Loads the (negated) the value of the operand into the accumulator |
|
|
| Stores the (negated) contents of the accumulator in the operand |
|
| Sets the operand (type |
| |
| Sets the operand (type |
| |
|
| Bitwise |
|
|
| Bitwise OR of the accumulator value and (negated) operand |
|
|
| Bitwise exclusive OR of the accumulator value and (negated) operand |
|
| Bitwise negation of the accumulator value | ||
|
| Addition of the accumulator value and the operand The result is written to the accumulator. |
|
|
| Subtraction of the operand from the accumulator value The result is written to the accumulator. |
|
|
| Multiplication of accumulator value and operand The result is written to the accumulator. |
|
|
| Addition of the accumulator value and the operand The result is written to the accumulator. |
|
|
| Checks if the accumulator value is greater than the operand value The result ( |
|
|
| Checks if the accumulator value is greater than or equal to the operand value The result ( |
|
|
| Checks if the accumulator value is equal to the operand value The result ( |
|
|
| Checks if the accumulator value is not equal to the operand value The result ( |
|
|
| Checks if the accumulator value is less than or equal to the operand value The result ( |
|
|
| Check if the accumulator value is less than the operand value The result (BOOL) is written to the accumulator. |
|
|
| Unconditional (conditional) jump to the specified jump label |
|
|
| (Conditional) call of a program or a function block (if the accumulator value is TRUE) |
|
| Exit the box and return to the calling box |
| |
|
| If the accumulator value is |
|
|
| If the accumulator value is |
|
| Evaluation of the reset operation |

Application | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
Multiple operands for one operator | . Options
| Variant 1:
Variant 2:  |
Complex operands | For a complex operand, you enter the opening bracket | A string is rotated by one character each cycle.  |
Function block call, program call | Column 1: Column 2: Name of the function block instance or program and opening bracket If no parameters follow, then the closing bracket Rows to follow that: Column 1: Parameter name followed by Column 2: Parameter value followed by a comma The closing bracket As a limitation according to the IEC standard, complex expressions cannot be used here. You need to assign such constructs to the function block or the program before the call. | 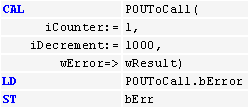 |
Function call | Line 1: Column 1: Column 2: Input variable Line 2: Column 1: Function name Column 2: Further input parameters separated by comma CODESYS writes the return value into the accumulator. Line 3: Column 1: | 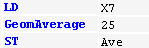 |
Action call | Like function block call or program call. The action name is appended to the name of the FB instance or the program. | 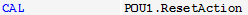 |
Jump | Column 1: Column 2: Name of the jump label of the destination network In the case of an unconditional jump, the preceding instruction sequence must end with one of the following commands: In the case of a conditional jump the execution of the jump depends on the loaded value. |  |
