Example: File over EtherCAT
Product: CODESYS EtherCAT
Description
This example shows how to read and write SDOs with CAN over EtherCAT as well as downloading a firmware file with File over EtherCAT. It also shows how to get information about the master and the slaves, such as the number of active slaves or the state of the slave. As hardware, two analog terminals with CAN over EtherCAT are used. The File-over-EtherCAT functions are implemented theoretically, without hardware.
Additional information
You can set various startup parameters for the device configuration. For devices which use CAN over EtherCAT, an index and a subindex are used for each parameter. For each parameter, you can read or write the value as a number or as a byte array with a maximum of four bytes.
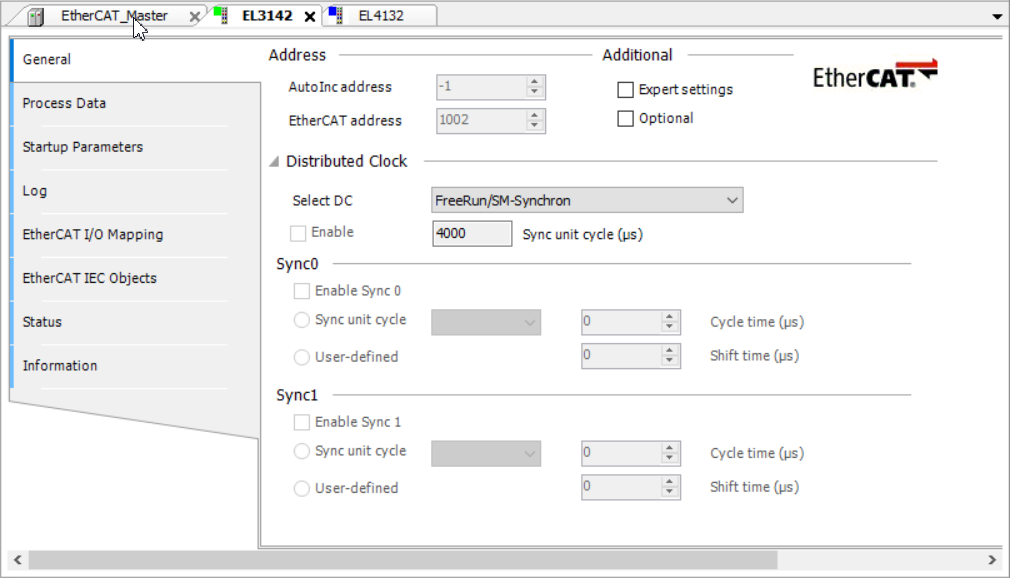 |
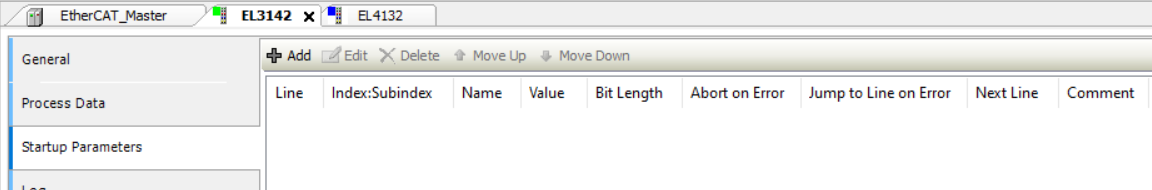
The parameters for EL4132 and EL3142 are set before startup. By double-clicking one of these devices, Startup parameters tab is shown. One start parameter is already set and you can use the New button to select more start parameters. The General tab shows the EtherCAT address which is used later to select the device. In the EtherCAT_Master tab under the General tab, you need to set the correct source address where the device is connected.
 |
CoE: First, the program has to wait until the EtherCAT Master is ready. After that the already set parameter is read from the device 1002 in a byte array and as DWORD. In addition, a parameter of four bytes is written and read afterwards. A parameter larger than four bytes is also written in this example.
So far, only the parameter values are used, but you can also read the complete entry into a byte array. These values are device-specific. All function blocks contain a udiSdoAbort variable. If an operation is canceled, then this variable returns an abort code. The error for this code can be found in the CANopen specification.
FoE: This function shows how to use File over EtherCAT to download a fictional firmware. After the EtherCAT Master is ready, memory for the complete firmware will be allocated. Then the specific slave is set to boot mode to download the firmware. When the download is finished, the memory will be released.
The upload function has no direct relation to the firmware example. It is just to show how the instance is called.
System requirements and restrictions
Programming system | CODESYS Development System (version 3.5.14.0 or higher) |
Runtime system | CODESYS Control Win (version 3.5.14.0) |
Add-on components | - |
Note
 DOWNLOAD Project
DOWNLOAD Project