Variable: VAR_IN_OUT
A VAR_IN_OUT variable is an input/output variable, which is part of a POU interface and serves as a formal pass-by-reference parameter.
Syntax
<keyword> <POU name>
VAR_IN_OUT
<variable name> : <data type>;
END_VAR
<keyword> : FUNCTION | FUNCTION_BLOCK | METHOD | PRGYou can declare an input/output variable in the VAR_IN_OUT declaration section in the POUs PRG, FUNCTION_BLOCK, METHOD, or FUNCTION. The VAR_IN_OUT variable can be read and written.
Call: When a POU is called, the formal
VAR_IN_OUTvariable receives the actual variable ("pass-by-reference variable") as the argument. At runtime, no copies are generated when parameters are passed. Instead, the formal variable receives a reference to the actual variable passed remotely. The referential variables contain a memory address internally as a value to the actual value (pass as pointer, call-by reference). It is not possible to specify a constant (literal) or a bit variable directly as an argument.Read/write access within the POU: If the variable is written to within the POU, then this affects the passed variable. When the POU is exited, any performed changes are retained. This means that a POU uses its
VAR_IN_OUTvariables just like the calling POU uses its variables. Read access is always permitted.Read/write access remotely:
VAR_IN_OUTvariables cannot be directly read or written remotely via<function block instance name>.<variable name>. This works only forVAR_INPUTandVAR_OUTPUTvariables.Passing string variables: If a string variable is passed as an argument, then the actual variable and the formal variable should have the same length. Otherwise the passed string can be manipulated unintentionally. This problem does not occur in the case of
VAR_OUTPUT CONSTANTparameters.Passing bit variables: A bit variable cannot be passed directly to a
VAR_IN_OUTvariable because it needs an intermediate variable.Passing of properties: Not permitted
Tip
If a string is passed as a variable or a constant to a formal VAR_IN_OUT CONSTANT variable, then the string is automatically passed completely. You do not have to check the string length.
For more information, see: "VAR_IN_OUT CONSTANT" Transfer Variable
Passing arrays
TYPE DUT_A :
STRUCT
xA: BOOL;
iB: INT;
END_STRUCT
END_TYPE
FUNCTION_BLOCK FB_SetArray
VAR_IN_OUT
aData_A : ARRAY[0..1] OF DUT_A; // Formal variable
END_VAR
aData_A[0].xA := TRUE;
aData_A[0].iB := 100;
PROGRAM PLC_PRG
VAR
fbSetA : FB_SetArray;
aSpecialData : ARRAY[0..1] OF DUT_A; // Actual variable
END_VAR
fbSetA(aData_A := aSpecialData);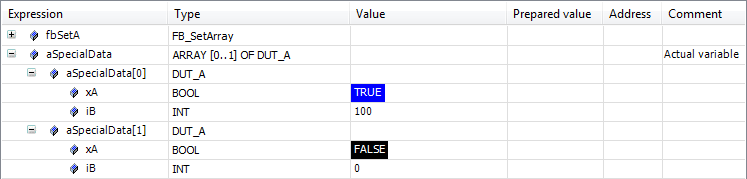
Passing strings
{attribute 'qualified_only'}
VAR_GLOBAL
g_sDEV_STATUS : STRING(25) := 'Device_A';
END_VAR
FUNCTION_BLOCK FB_SetStatus
VAR_IN_OUT
sDeviceStatus : STRING(25); // Formal parameter
END_VAR
sDeviceStatus := CONCAT(sDeviceStatus, ' Activ');
PROGRAM PLC_PRG
VAR
fbDoB : FB_SetStatus;
END_VAR
fbDoB(sDeviceStatus := GVL.g_sDEV_STATUS); //Call with actual parameterThe variable sDeviceStatus is part of the POU interface of FB_B. When calling fbDoB, first a device name is assigned to the string and then the string is manipulated.

Passing bit variables
VAR_GLOBAL
xBit0 AT %MX0.1 : BOOL;
xTemp : BOOL;
END_VAR
FUNCTION_BLOCK FB_DoSomething
VAR_INPUT
xIn : BOOL;
END_VAR
VAR_IN_OUT
xInOut : BOOL;
END_VAR
IF xIn THEN
xInOut := TRUE;
END_IF
PROGRAM PLC_PRG
VAR
xIn : BOOL;
DoSomething_1 : FB_DoSomething;
DoSomething_2 : FB_DoSomething;
END_VAR
// The following line of code causes a compiler error:
// C0201: Typ 'BIT' is not equal to type 'BOOL' of VAR_IN_OUT 'xInOut'
DoSomething_1(xIn := xIn, xInOut := xBit0);
// Workaround
xTemp := xBit0;
DoSomething_2(xIn := xIn, xInOut := xTemp);
xBit0 := xTemp;The program calls the function block instances DoSomething_1 and DoSomething_2. As a result of the direct assignment of the bit variable xBit0 to the VAR_IN_OUT input, a compiler error is generated when the DoSomething_1 instance is called. In contrast, calling the DoSomething_2 instance with the assignment of an intermediate variable is correct code.
Transfer variable VAR_IN_OUT CONSTANT
A VAR_IN_OUT CONSTANT variable serves as a constant pass-by-reference parameter, to which a STRING or WSTRING type variable or constant (literal) can be passed. The parameter can be read, but not written. Passing of properties is not permitted.
Syntax declaration
<keyword> <POU name>
VAR_IN_OUT CONSTANT
<variable name> : <data type>; // formal parameter
END_VAR
<keyword> : FUNCTION | FUNCTION_BLOCK | METHOD | PRGVAR_IN_OUT CONSTANT variables are declared without assigning an initialization value.
When calling the POU, a
STRINGorWSTRINGconstant variable or literal can be passed. Consequently, write access is not permitted.Passing parameters of a string constant: The string length of the constants can be any size, and the string length does not depend on the string length of the
VAR_IN_OUT CONSTANTvariables.
Tip
If the Replace constants option is selected in in the Compile Options category, then passing the parameters of a constant with basic data type or a constant variable with basic data type generates a compiler error.
Tip
The variable is supported in compiler version >= 3.5.2.0.
Passing parameters of string constants and string variables
FUNCTION funManipulate : BOOL
VAR_IN_OUT
sReadWrite : STRING(16); (* Can be read or written here in POU *)
dwVarReadWrite : DWORD; (* Can be read or written here in POU *)
END_VAR
VAR_IN_OUT CONSTANT
c_sReadOnly : STRING(16); (* Constant string variable can only be read here in POU *)
END_VAR
sReadWrite := 'String_from_POU';
dwVarReadWrite := STRING_TO_DWORD(c_sReadOnly);
PROGRAM PRG_A
VAR
sVarFits : STRING(16);
sValFits : STRING(16) := '1234567890123456';
dwVar: DWORD;
END_VAR
// The following line of code causes the compiler error C0417:
// C0417: VAR_IN_OUT parameter 'sReadWrite' needs a variable with write access as input.
funManipulate(sReadWrite:='1234567890123456', c_sReadOnly:='1234567890123456', dwVarReadWrite := dwVar);
// Correct code
funManipulate(sReadWrite := sValFits, c_sReadOnly := '23', dwVarReadWrite := dwVar);
funManipulate(sReadWrite := sVarFits, c_sReadOnly := sValFits, dwVarReadWrite := dwVar);In the code, strings are passed to the funManipulate function via different VAR_IN_OUT variables. When passing a string literal, a compiler error is output to a VAR_IN_OUT variable. When passing a constant variable to a VAR_IN_OUT CONSTANT variable, correct code is generated even for passing string variables.