The IEC application cannot open any more file handles.
Important
Before you change the limit for file handles on your system, you should urgently consider the consequences for all services on your Linux system. Instead, we recommend finding the cause of the leak.
Troubleshooting
Loss of license status. The WIBU license is broken after a certain period of time.
New files cannot be opened.
The default behavior of Linux processes is to allow a maximum number of open file handles. When a process reaches this limit, no more new files can be opened.
You can check the limit value of your system with the console command:
ulimit -n
Every process in Linux has a process ID and the kernel provides detailed information about each process in its file/folder system procfs. This allows you to easily determine the number of file handles which one process has at any given time.
Find the process ID of the CODESYS runtime environment.
You can use standard Linux tools to find the process ID of the CODESYS runtime environment:
htopnormally displays the process ID in the first column (PID).topnormally displays the process ID in the first column (PID).You can combine the
psandgrepcommands for a quick search:ps aux | grep codesyscontrol
Take note of the process ID and use it in the following commands where the placeholder
<pid>is used.Check and monitor the file handles.
Now list the entries in
procfsto see the file handles of the runtime process.sudo ls -la /proc/<pid>/fd/Example 10. This may look as follows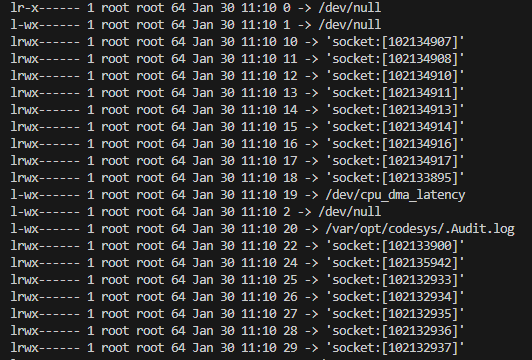
If the file handles are "real" files, then you can see the path. Other file handles could be sockets or similar.
If you execute this command multiple times one after the other, then you can observe whether you have an increasing number of file handles and which files are open.
The
watchcommand creates a view which is updated every 2 seconds.watch sudo ls -la /proc/<pid>/fd/
These actions can help you monitor the open handles and therefore find out which files could be involved in the file handle leak.