Diagnosis – Error Cases
The following section deals with possible error cases and how these are handled based on the diagnosis values:
Exceeding the cycle time of the application
If the execution time exceeds the cycle time or is close to exceeding the set cycle time, then the diagnosis for the cycle timeout may be triggered.
In the following example, the execution time of the application task is significantly shorter than the set cycle time. Because the application task has a lower priority than the Time Provider receive task, it is interrupted with each received package, which also affects the execution time. The communication task has the lowest priority and is always processed after the application task.
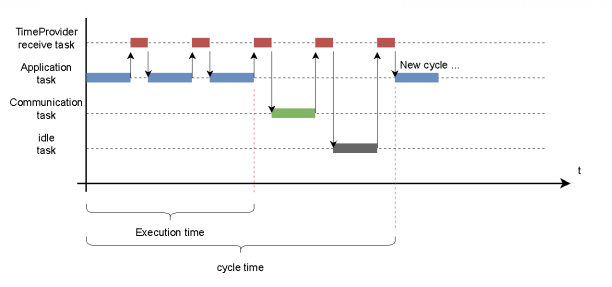 |
The diagnosis value IEC execution time shows the minimum, maximum, and average execution time of the application task on the system. This should be significantly less than the set cycle time for the application.
In CODESYS Safe Control, the cycle time is monitored using local timestamps and Time Provider timestamps, and if the cycle time is exceeded by more than 5%, then one of the following exception errors will be thrown:
Exception ID: 0x40000065: Exception channel 1: Plausibility check of the local timestamp interval: <interval of local timestamp> to the cycle time: <cycle time> (Deviation: <deviation>, Deviation tolerance: <maximum allowed deviation>)
Exception ID: 0x40000066: Exception channel 1: Plausibility check of the remote timestamp interval: <interval of the remote timestamp> to the cycle time: <cycle time> (Deviation tolerance: <maximum allowed deviation>)
Delay of the application task
If the execution of the application task is delayed, for example by a task with a higher priority, then the diagnosis for the cycle timeout may be triggered.
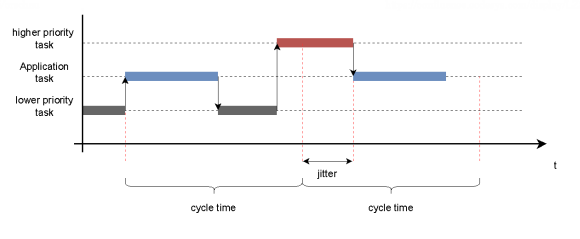 |
The diagnosis value IEC task jitter shows the minimum, maximum, and average task jitter of the application task on the system. This should be as small as possible so that the application task is executed as close as possible to the expected time.
In CODESYS Safe Control, the cycle time is monitored using local timestamps and Time Provider timestamps. If the delay of the execution is exceeds more than 5% of the cycle time, then one of the following exceptions will be thrown:
Exception ID: 0x40000065: Exception channel 1: Plausibility check of the local timestamp interval: <interval of local timestamp> to the cycle time: < cycle time> (Deviation: <deviation>, Deviation tolerance: <maximum allowed deviation>)
Exception ID: 0x40000066: Exception channel 1: Plausibility check of the remote timestamp interval: <interval of remote timestamp> to the cycle time: <cycle time> (Deviation tolerance: <maximum allowed deviation>)
Delay of the Time Provider packages
The delay of the Time Provider packages can occur at different locations in the system:
The Time Provider is called with a delay.
The Time Provider package is delayed during transmission.
The Time Provider receive task is delayed.
When monitoring in the CODESYS Safe Control, all three cases lead to the following exception errors:
Exception ID: 0x40000067: Exception channel 1: Plausibility check of remote timestamp interval: <interval of remote timestamp> to local timestamp interval: <interval of local timestamp> (Deviation: <deviation>, Deviation tolerance: <maximum allowed deviation>)
This involves monitoring the difference between the intervals since the last received package.
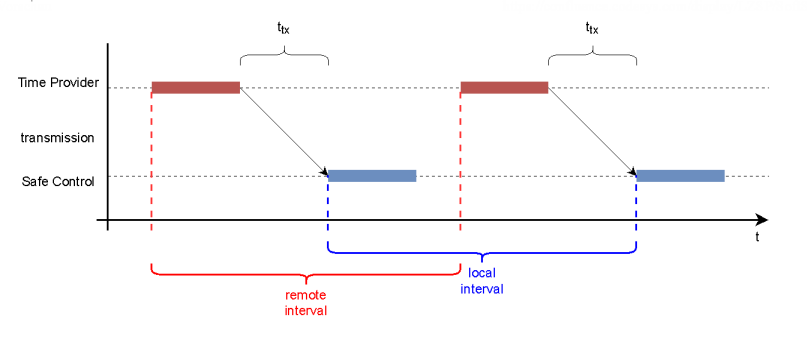
The diagnosis value TP sample interval shows the minimum, maximum, and average time interval elapsed since the last received package. This is measured using the local timestamp, which is determined each time a Time Provider package is received. The diagnosis value TP remote interval shows the same time interval, but this is measured using the timestamps in the received Time Provider packages.
Ideally, these values should differ only slightly from each other.
Assuming a constant transmission, the transmission time cancels out in the time measurement.
 |
Delay in the execution of the Time Provider
If the execution of the Time Provider is delayed, then the remote interval is extended for a constant transmission time (ttx). This is seen in the increased or highly fluctuating diagnosis value TP remote interval.
Neither the transmission time (ttx) nor other factors in CODESYS Safe Control have an impact on this value because it is calculated based only on the timestamps stored in the Time Provider packages.
The more even and constant the TP remote interval values are, the more reliably the Time Provider runs.
Delayed transmission of Time Provider packages
If the Time Provider packages are delayed when being transmitted, then the Local Interval is extended for the constant execution of the Time Provider. This is seen in the increased diagnosis value TP local interval.
This includes both the network transmission path and the correct scheduling of the Time Provider receive task. The value Local Interval is calculated using the local timestamps, which have been determined immediately after receiving a Time Provider package.
An uneven and highly fluctuating TP local interval diagnosis value indicates a problem with the transmission or prioritization of the Time Provider receive task on the CODESYS Safe Control.